Clean Energy energy management
There is a separate vehicle network with two additional batteries for the range of functions of the CE module. This ensures an independent power supply for each channel of the CE module.
Overview
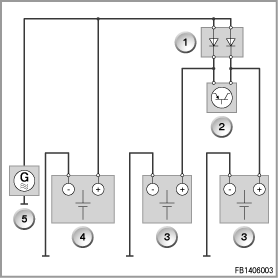
The following principle drawing provides an overview of the vehicle circuit structure in the CE vehicle.
- Inhibiting diodes. The inhibiting diodes ensure that CE auxiliary batteries cannot discharge via the vehicle electrical system. The CE auxiliary batteries thus supply exclusively the CE module and the CE components connected to the CE module.
- CE module. The connected battery sensors (IBS) enable the CE module to pick up the state of charge of the CE batteries
- CE batteries. For safety reasons, there are two batteries. Each battery supplies a channel of the CE module. Each CE battery has its own additional battery sensor (IBS = Intelligent Battery Sensor) that transfers the battery status data to the CE module.
- Vehicle battery. The vehicle battery supplies all the electrical consumer in the vehicle electrical system.
- Vehicle electrical system with alternator. The alternator charges all the batteries in the vehicle.
Notes on safety
The CE batteries are part of the safety concept in the CE vehicle, as they provide the power supply for the CE sensors and actuators.
Disconnecting or discharging the batteries means that the vehicle can no longer be monitored for gas alarms.
The following points must be observed without fail in the context of the CE batteries:
- Ensure that a battery charger is always connected on the vehicle when the vehicle is in the workshop. Connect the charger at central charge support point in the engine compartment.
- The inhibiting diodes mean there is a voltage drop from 0.2 to 0.3 V in the CE vehicle network. For this reason, a charge voltage of 14.8 V must be set at the battery charger.
- If a CE battery is disconnected or replaced, it must be ensured that the CE battery is fully charged before in is installed! To this end, connect the CE battery to a battery charger and charge or recharge it in all cases prior to installation.
- If the battery sensor (IBS) of a CE battery is replaced, it must also be ensured that the CE battery is fully charged before installation of the new IBS sensor.
- It is only ensured that CE batteries cannot discharge via the vehicle electrical system is the inhibiting diodes are free of faults. For this reason, the inhibiting diodes must be checked every 3 months within the framework of maintenance.
The check must be carried out after completion of all work on the vehicle.
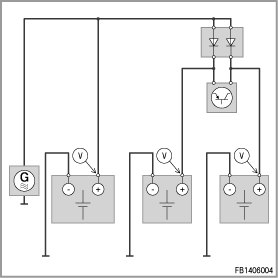
Check of the CE inhibiting diodes
The CE inhibiting diodes can be checked as follows:
- Stop all work on the vehicle.
- Disconnect the battery charger.
- Start the engine (operating mode petrol or hydrogen).
- Measure the voltage of the vehicle battery.
- Measure the voltage of the CE batteries.
The inhibiting diodes are OK if the measured battery voltage of the CE batteries is 0.2 V to 0.3 V lower than the measured battery voltage of the vehicle battery.
Determining the charge state
Intelligent battery sensors (IBS)
To determine the state of charge of the CE batteries, two battery sensors (IBS) are fitted. The IBS pick up the charge and discharge currents of the batteries (current balance).
In order to draw conclusions regarding the state of charge (SoC) of the batteries, it is required to know the general battery condition. This is done by means of an open-circuit voltage measurement.
Open-circuit voltage measurement
The open-circuit voltage measurement is also carried out by the battery sensors (IBS) if the CE vehicle network is in the closed-circuit current mode (CE module asleep). The system-specific characteristics of the CE vehicle network in the closed-circuit current mode are taken into account (see document 'Closed-circuit current characteristics of CE vehicle network).
To run the open-circuit voltage measurement, the following requirements must be met:
- Operating pressure in the hydrogen tank greater than 3.3 bar
- Fill level of hydrogen at least 2000 g
A complete open-circuit voltage measurement takes 2.5 hours.