Closed-circuit current characteristics in the CE vehicle network
The closed-circuit current characteristics in the CE (Clean Energy) vehicle network have a number of special features. These must be considered when a closed-circuit current test is carried out for the CE vehicle network.
Closed-circuit current test
A closed-circuit current test of the CE vehicle network is only possible with the oscilloscope - recorder mode. The 50 A current measuring clip is used for the measurement.
Preparing the measurement
Connect the measurement system interface box (MIB) to the GT-One. Connect the 50 A current measuring clip to the MIB. Do not connect the current measuring clip to the vehicle yet.
- Select 'Measurement system', 'Oscilloscope settings' screen; enable recorder mode.
- Select 50 A current, set the measuring range at 10 A.
- Set the frequency range.
The frequency range determines the recording duration and the number of measurements per second.
- Select the oscilloscope display. The measurement is started
- Confirm calibration of the current measuring clip with 'OK'. Then connect the current measuring clip to the B+ cable of a CE battery.
Note: The CE vehicle network is 'isolated' from the vehicle electrical system by two diodes (see functional description for the CE vehicle network). During the closed-circuit current test of the CE vehicle network, make sure that the current measuring clip is connected ”within” the CE vehicle network.
Set frequency range
|
Number of measurements
|
Maximum duration of recording
|
2 MHz
|
1 per second
|
83 minutes
|
1 MHz
|
1 every 2 seconds
|
2.7 hours
|
0.4 MHz
|
1 every 5 seconds
|
5.5 hours
|
0.1 MHz
|
1 every 20 seconds
|
27.7 hours
|
Measuring notes
Connecting the current measuring clip to the B+ cable creates a current impulse that can be seen in the oscilloscope display. Ignore this impulse.
A change in the frequency range is only possible if the ongoing measurement recording is terminated. After a new start to the measurement, a new calibration of the current measuring clip is carried out. The current measuring clip must be removed from the B+ cable for a short time.
Before the closed-circuit current measurement, disconnect the diagnostic head from the vehicle.
Important A precondition for error-free closed-circuit current characteristics is that all gas sensors are correctly connected and no faults have been stored for the gas sensors. Any faults that are present must be remedied before the measurement.
Closed-circuit current sequence
The following description covers the closed-circuit current sequence in the CE vehicle network after the vehicle electrical system has gone to sleep.
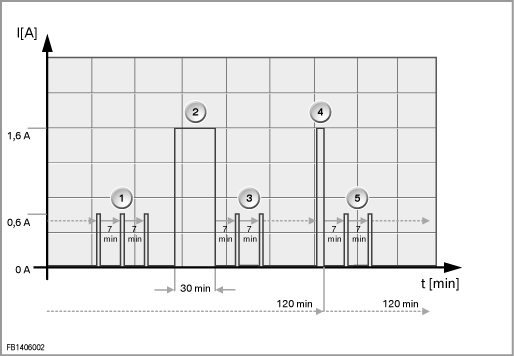
- After the vehicle electrical system has gone to sleep, the CE vehicle network remains awake for a short time (after-run). The measured current is a maximum of 1.6 A. The following after-run times are possible:
10 minutes after engine operation.
30 seconds if there was no engine operation in the last awake phase.
- After the after-run has finished, a closed-circuit current of approx. 0.5 mA is set (measured current with 50 A ammeter clip approx. 0 mA).
16 minutes after the vehicle electrical system has gone to sleep, the CE vehicle network is wakened by the power module in that it sends the command 'consumer shutdown'. This awake phase (current approx. 1.6 A) lasts a maximum of 2 minutes.
- 7 minutes after the command ”consumer shutdown”, the cyclical monitoring of the vehicle for gas alarm starts. Every 7 minutes, the CE module is partially wakened (semi-sleep) for approx. 1.5 seconds. The current is approx. 0.6 A.
Note: If the CE module detects a fault in one or more gas sensors, the CE module is wakened completely every 7 minutes. The current is then approx. 1.6 A for 1.5 seconds.
- After 2 hours (120 minutes) or 7 hours (420 minutes), the CE module is wakened for 15 seconds (rise in current up to approx. 1.6 A). During this time, a system check is carried out. The system check is repeated every 2 hours (120 minutes).
Waking takes place after 7 hours if the engine was operated with hydrogen in the preceding awake phase.
- 7 minutes after the system check, the cyclical monitoring of the vehicle for gas alarm starts again.
- Every 2 hours, the CE module is wakened and a system check is carried out.
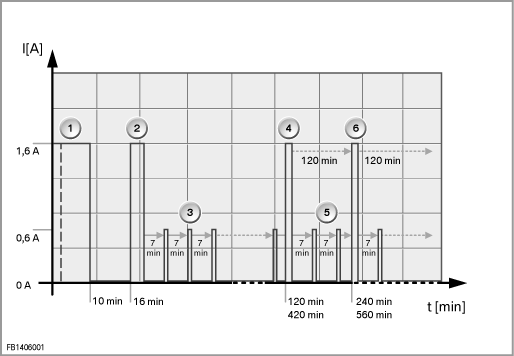
Activating of the boil-off management in the closed-circuit current mode
In stationary operation, the pressure in the hydrogen tank can rise to such an extent (> 5.3 bar overpressure) that hydrogen has to be withdrawn by the boil-off management. If this is the case, the CE module is wakened.
- Ongoing sleep phase with 7-minute monitoring for gas alarm.
- Waking up the CE module and activating the boil-off management after an increase in pressure in the tank. In the awake phase, the current rises to 1.6 A. The boil-off mode lasts a maximum of 30 minutes.
- Subsequently, the sleep phase with 7-minute monitoring for gas alarm starts again.
- 2 hours (120 minutes) after the last system check, a 15-second system check is run again.
- Continued sleep phase with cyclical monitoring for gas alarm.
Carrying out the measurement
The following testing procedure is recommended:
- 1. Measurement - frequency setting 2 mHz.
Assessment of the first closed-circuit current phase and check whether during the cyclical gas monitoring the current rises to a maximum of 0.6 A. If the current rises to 1.6 A here, one of the gas sensors is faulty.
- 2. Frequency setting - frequency setting 0.1 mHz.
Assessment of the closed-circuit current characteristics over at least 7 hours. Check whether the specified maximum times for the system check or the boil-off phases are adhered to.
Note: With the stated frequency setting, a measured value is recorded only every 20 seconds. It should therefore be borne in mind that not all semi-awake phases (gas monitoring, duration a maximum of 1.5 seconds) or not all awake phases for the system check (duration 15 seconds) are recorded.