The MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport) network uses a ring bus for data communication between the various control modules. Signal transmission is by means of fiber-optic cable. Data transmission on the ring bus takes place in one direction only. On the MOST ring, messages can only be transmitted provided the bus ring is complete and fully functional. If there is a ring fault in the MOST network, the system can only communicate with the Multi Audio System Controller (or Car Communication Computer. This is possible because the control module is directly connected to the K-CAN data bus. There is a transmission and a reception module (transmitter and receiver) as a unit in each MOST control module for connecting to the MOST bus. The unit has an integrated transmit and receive diode. The optical testing and programming system can be used to test the transmitter and receiver of a control module.
If there is a ring fault (defect between two control modules), the following fault patterns can occur:
The above faults can also occur in combination with each other. When there is a ring fault, the first task is to locate the two control modules between which the ring fault has occurred. This is established using the ring fault diagnosis. In order to be able to identify the fault precisely, ring fault diagnosis must be followed by a check of the power supply. If the power supply is OK, the defect can only be established using the optical test. The test program for the optical test on the MOST bus (or ring fault diagnosis, as the case may be) can be found under function selection: Body, Bus Functions, MOST Functions and Optical Test (or Ring Fault Diagnosis).
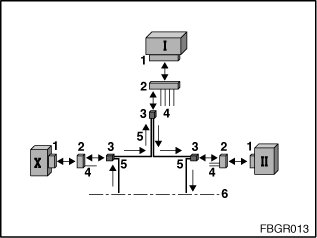
Transmission direction in the MOST ring
Messages are transmitted from the Multi Audio System Controller (or Car Communication Computer) towards the CD changer, amplifier, ..., video module, ... and back to the Multi Audio System Controller (or Car Communication Computer).
In the MOST ring, the sockets (1) and connectors (2) for each of the MOST control modules are different. Only the two-pin fiber-optic cable connector (3) is the same for all MOST control modules. This means that two adapters are required for the optical test on the MOST bus.

Fig. 1: Overview of the plug-in connections from the MOST ring
I: Multi Audio System Controller (or Car Communication Computer) |
II, X: MOST control module according to car equipment |
1: Socket for control module |
2: Connector for control module |
3: Two-pin fibre-optic cable connector pinned from control-unit plug (2) |
4: Power supply and other cables |
5: Fiber Optics |
6: Other MOST control modules according to car equipment |
The optical testing and programming system
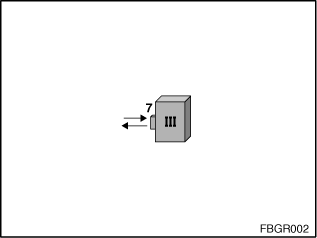
Fig. 2: Optical testing and programming system (III)
III: Optical testing and programming system |
7: Socket for mounting the MOST adapter |
The optical testing and programming system (MOST section) has a socket for connection to the MOST adapters.
For the optical test of a control module (or fibre-optic cable), the control module (or fibre-optic cable) must be connected to the optical testing and programming system using an adapter. However, each adapter has a different attenuation value. So that these different attenuation values are taken into account in the optical test, calibration must be carried out before each optical test. During the calibration, there is also a check as to whether the adapter is OK. The various calibrations, depending on whether a MOST control module or a fiber-optic cable is being tested, are shown below.
Calibration for the test of the MOST control module:To test a MOST control module, you need the MOST control module cable (A1 = 663122). For calibration, you connect the MOST control module cable (A1) to:
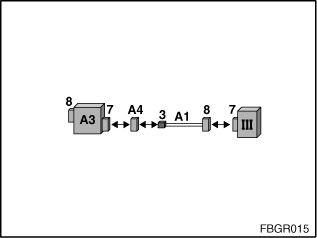
Fig. 3: Calibration for the test of the MOST control module
III: Optical testing and programming system |
3: Two-pin fibre-optic cable connector |
7: Socket for mounting the MOST adapter |
8: Connector from MOST adapter or test loop |
A1: 663122 |
A3: 663124 |
A4: 663125 |
|
Calibration for the test of the fibre-optic cable: To test the fibre-optic cable, the MOST wiring harness extension is required (A2 = 663123). For the calibration, the MOST wiring harness extension (A2) is connected to:
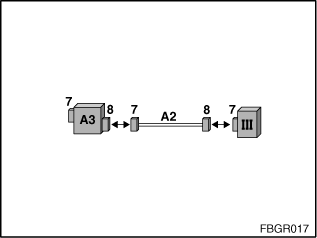
Fig. 4: Calibration for the test of the fiber-optic cable
III: Optical testing and programming system |
|
7: Socket for mounting the MOST adapter |
8: Connector from MOST adapter or test loop |
A2: 663123 |
A3: 663124 |
For the optical test of a control module (or fibre-optic cable), the control module (or fibre-optic cable) must be connected to the optical testing and programming system using an adapter. The two adapters required for this test are shown in the following.
Test of the MOST control module:To test a MOST control module, (II) the MOST control module cable is required (A1 = 663122). Procedure for testing a MOST control module:
In order to disconnect the two-pin fiber-optic cable connector (3) from control module connector (2), it might be required to disconnect the control module connector (2) from the socket (1) first. Then run the operation as described under 1 to 3 and on completion connect control module connector (2) with socket (1).
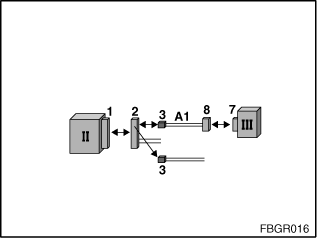
Fig. 5: Test of the MOST control module
II: MOST control module |
III: Optical testing and programming system |
1: Socket for control module |
2: Connector for control module |
3: Two-pin fibre-optic cable connector pinned from control-unit plug (2) |
7: Socket for mounting the MOST adapter |
8: Connector from MOST adapter |
A1: 663122 |
Test of fibre-optic cable: To test the fibre-optic cable, the MOST wiring harness extension (A2 = 663123) and plug housing are required (A4 = 663125). Procedure for testing the fiber-optic cable:
In order to disconnect the two-pin fiber-optic cable connector (3) from control module connector (2), it might be required to disconnect the control module connector (2) from the socket (1) first.
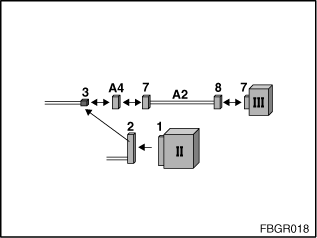
Fig. 6: Test of fiber-optic cable
II: MOST control module |
III: Optical testing and programming system |
1: Socket for control module |
2: Connector for control module |
3: Two-pin fibre-optic cable connector pinned from control-unit plug (2) |
7: Socket for mounting the MOST adapter |
8: Connector from MOST adapter |
|
A2: 663123 |
A4: 663125 |
Note:
To test the fiber-optic cable, the two-pin fiber-optic cable must be disconnected from a MOST control module and connected to the OPPS device. If, for example, you wish to test the fiber-optic cable between the amplifier and the video module, the fiber-optic cable must be disconnected from the video module and connected to the OPPS device.
If a fiber-optic cable is disconnected in the MOST ring, a red light flashes at the exit of the fiber-optic cable. The Multi Audio System Controller (or Car Communication Computer) attempts namely, with the fiber-optic cable disconnected, to wake up the MOST bus using the flashing light. To test the fiber-optic cable, the two-pin fiber-optic cable must be disconnected from a MOST control module and connected to the OPPS device. However, the test of the fiber-optic cable only leads to a correct conclusion if an exit flashes when the fiber-optic cable is disconnected.
It is namely the case when testing the fiber-optic cable that if, for example, a MOST control module in the MOST ring or a second section of fiber-optic cable in front of the tested fiber-optic cable in the MOST ring is defective, then the MOST ring cannot be optically closed. This is why the fault ”no flashing light” at the exit of the fiber-optic cable can have the following causes:
In order to localize the cause of the fault, perform the following steps:
Disconnect another fiber-optic cable in front of the fiber-optic cable in the MOST ring (where there is no flashing light at the exit) and check whether you can see a flashing light at the exit:
Note:
If the display of the light output fluctuates during the test of the fiber-optic cable, it is highly likely that there is another defective point after the tested fiber-optic cable in the MOST ring. The cause is that the ring is not closed and there is thus no continuous light in the ring, rather pulsed light (when the MOST ring is interrupted, the Multi Audio System Controller (or Car Communication Computer) attempts to wake up the MOST bus using a flashing light).